What is Actin and Myosin?
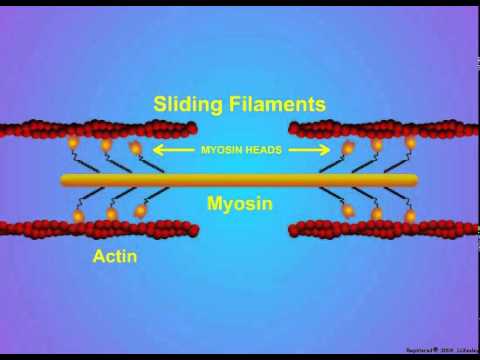
Both actin and myosin are proteins found in all types of muscle tissue. Muscle contractions and movement are caused by the interaction of thick myosin filaments and thin actin filaments.
Myosin is a form of molecular motor that turns ATP’s chemical energy into mechanical energy.
The actin filaments are subsequently pulled along by the mechanical energy, causing muscle fibers to contract and generate movement.
For better Understanding: Myosin and actin are two proteins found in all forms of muscle tissue. Actin forms thin filaments, while myosin forms large filaments. The filaments of actin and myosin work together to generate force. This force causes muscle cell contractions, which allow muscles and thus body structures to move more easily.
Difference between Actin and Myosin
Actin is a protein that forms thin contractile filaments within muscle cells, whereas myosin is a protein that makes thick contractile filaments within muscle cells.
Muscle types: presence of Actin and Myosin
Muscle is a type of contractile tissue found in animals that has the primary purpose of facilitating movement.
Muscle tissue can be divided into three categories in the human body:
Skeletal muscle is a type of muscle that is linked to bones. It is the most common form of muscle tissue in the human body, as well as the only one that can be moved voluntarily. Skeletal muscle contractions pull on the skeleton’s bones, allowing them to move (together with the bodily structures they support).
Smooth muscle is located in the internal organs, excluding the heart, and blood arteries and contracts involuntarily.
Cardiac muscle is a type of muscle that only exists in the heart and contracts automatically A&M filaments are found in all three muscle types and work together to produce muscular contractions.
Also Read: Know about your personality if you have round front teeth
How Exercise can help in managing these proteins
A person has practically all of the muscle cells at birth or shortly after. Individual cells, on the other hand, can get larger and their internal machinery can be upgraded through exercise.
There are two main ways to exercise, each with its own set of benefits.
1. Distance jogging is a low-intensity, long-duration workout that improves endurance without increasing power.
2. Weight lifting, for example, is a high-intensity, short-duration activity that builds power but not endurance.
There are three types of muscle cells, each of which is impacted differently by exercise. Muscle cells develop more mitochondria, the internal factories that use food and oxygen to make the energy-carrying molecule as a result of endurance-building exercise.
Exercise also promotes the formation of new blood vessels in the muscle, which helps to better transport oxygen and nutrients while also removing waste materials.
Also Read: OVAL SHAPED TEETH – the shape for disciplined and organized people