Welcome, students, parents or teachers in this article we are going to State five differences between bhangar and khadar with Definition. Take a note that in exams you can add more points in answer to score more. To earn extra marks you can explain it in about 300 words. Thanks for reading the answer.
State five differences between bhangar and khadar with Definition
State five differences between bhangar and khadar and explanation:
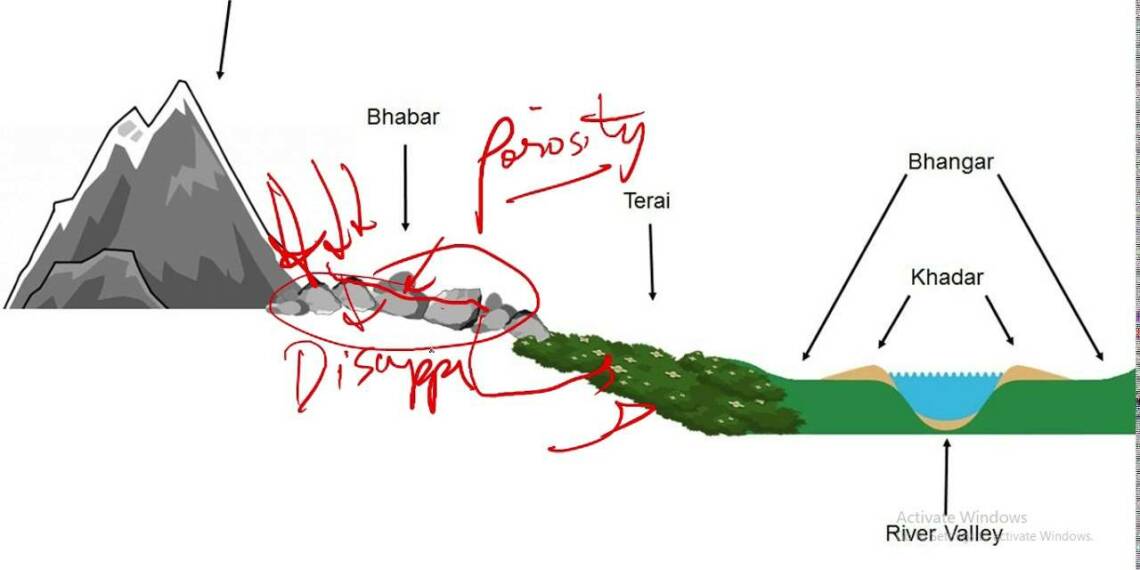
Soil Type: Bhangar is a term used to refer to the older, higher terrace of land, while khadar refers to the younger, lower terrace of land.
Age: Bhangar is older and more stable than khadar.
Elevation: Bhangar is usually found at a higher elevation than khadar.
Soil Composition: Bhangar has a thick layer of clay and silt, while khadar has a thinner layer of alluvium.
Flooding: Khadar is more prone to flooding than bhangar. Due to its lower elevation, khadar is more susceptible to flooding during the monsoon season.
Also Read: 10 Difference between Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats
Definition
Bhangar and Khadar are terms used to describe the different types of soil found in the floodplains of the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers in India.
Bhangar is the older, upland soil found on the higher ground in the floodplain. It is composed of clay and silt, and is generally less fertile than the khadar soil.
Khadar is the newer, lowland soil found on the lower ground in the floodplain. It is composed of sand and silt, and is generally more fertile than the bhangar soil. It is deposited by the annual floods from the Ganges and Brahmaputra rivers, providing rich nutrients for agriculture.
In summary, Bhangar is older and less fertile soil, while Khadar is newer and more fertile soil.