Welcome, students, parents or teachers in this article we are going to give you the answer of What is shifting cultivation what are its 5 disadvantages? Take a note that in exams you can add more points in answer to score more. To earn extra marks you can explain it in about 300 words. Thanks for reading the answer.
What is shifting cultivation what are its 5 disadvantages?
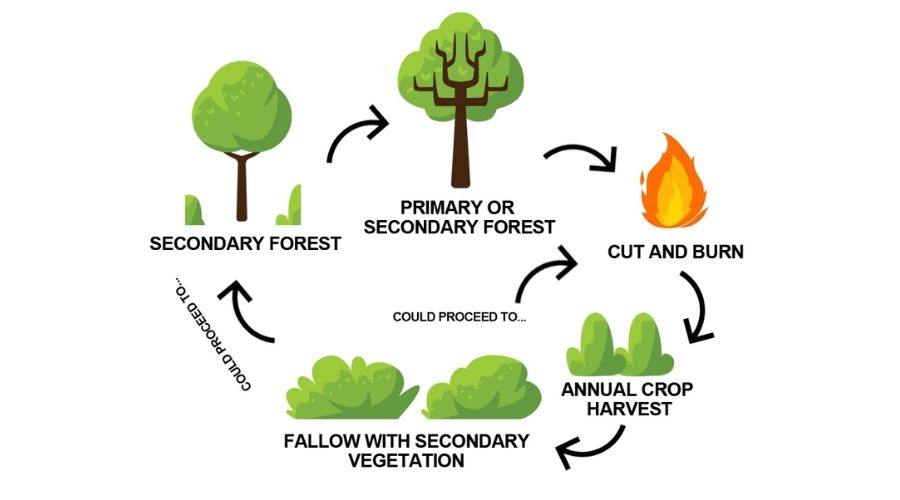
Shifting cultivation is a traditional agricultural system that involves the clearing of forest land for crop production, followed by abandonment of the field and relocation to a new area once soil fertility has declined.
Shifting cultivation is a type of agriculture that involves moving from one plot of land to another and cultivating different crops in each plot. This type of agriculture is commonly practiced in tropical regions with poor soil fertility, where farmers must move to new plots of land in order to allow the soil to regenerate after several years of cropping.
The process typically involves clearing a plot of land, burning the vegetation, and then planting crops. After a few years, the soil will become depleted and the farmer will move to a new plot and repeat the process.
Also Read: What Are Barchans Where Are They Found: Unraveling the Mystery
What is shifting cultivation what are its 5 disadvantages?
Soil degradation: Constant clearing of forest land and intensive cropping lead to soil degradation and loss of fertility over time.
Biodiversity loss: Clearing large areas of forest results in the loss of biodiversity, including the destruction of habitats for wildlife and the loss of plant species.
Low crop yields: Shifting cultivation often results in low crop yields due to poor soil fertility, poor crop management, and a lack of resources for investment in the fields.
Also Read: Let’s Define: Demystifying the Concept of Threshold Frequency
Environmental degradation: The burning of forest land for crop production releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and contributes to climate change.
Conflict: Shifting cultivation often leads to conflicts between farmers and forest-dependent communities who rely on the forest for their livelihoods. In addition, conflicts can arise between farmers over the use of land and resources, particularly as population densities increase.
Also Read: What is Red and yellow soil? 7 benefits of the soil