In the world of chemistry: State the modern periodic law
State the modern periodic law: In the world of chemistry, the periodic table is a fundamental tool for understanding the properties of elements. The Modern Periodic Law is a principle that organizes these elements in a unique and insightful way. Join me as we dive deeper into state the modern periodic law and unravel its significance in the realm of chemistry.
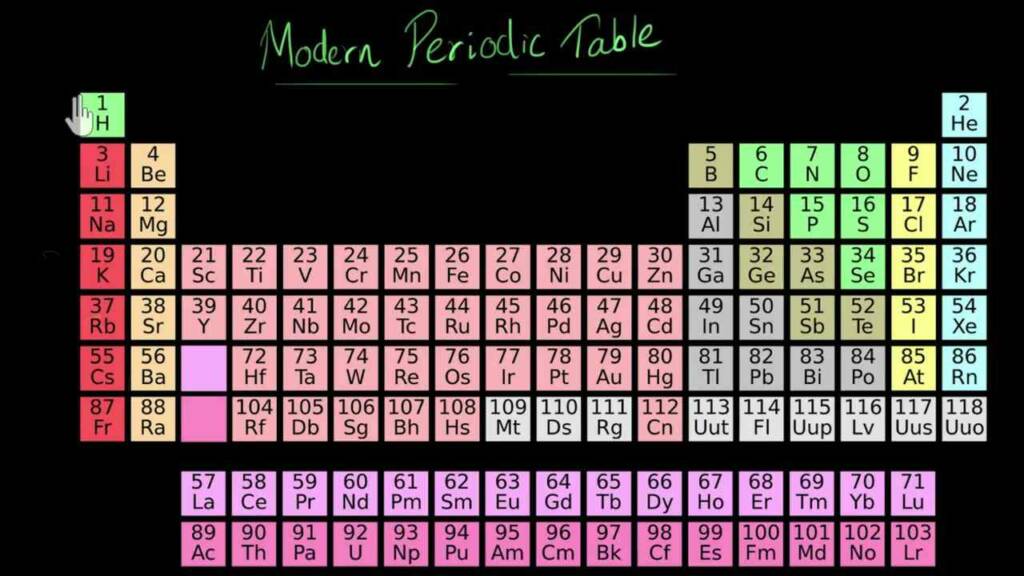
The modern periodic law states that an element’s physical and chemical characteristics are periodic functions of its atomic number. It was first put forth by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. This law is based on the periodic table’s arrangement of elements, which places substances with comparable properties in vertical columns or groups.
Periods, which are horizontal rows of elements arranged in increasing atomic number order, are the divisions of the periodic table. The atomic number of the elements rises along with the number of protons in the nucleus as you move from left to right across a period. As a result, the number of electrons in the atoms’ outermost energy level, or valence shell, rises in proportionally.
As you move from one element to the next in a period, the characteristics of those elements gradually change, and patterns or trends start to emerge. As the nuclear charge increases, the electrons are drawn more strongly to the nucleus and the size of the atoms typically decreases from right to left over a period. As a result, the ionisation energy and electron affinity rise while the atomic radius decreases.
Also Read: What is lactometer and its working?
The characteristics of the elements in a group, or column, of the periodic table, on the other hand, are comparable to one another but distinct from those of the elements in other groups. The same group of elements share the same number of valence electrons, which govern the chemical properties of the elements. As a result, this phenomenon occurs. For instance, group 1’s alkali metals, which all have a single valence electron, are very reactive and can quickly lose that electron to form a positive ion.
A framework for comprehending the characteristics and behaviour of the elements, as well as their chemical reactions and bonding, is provided by the modern periodic law. It enables scientists to design new materials with particular properties for a variety of applications as well as predict the properties of new elements. As a result, it is a fundamental idea in chemistry and the foundation for much of what we currently know about the physical universe.
Follow our google news publication for more news and daily updates: @tfipost