The European Union and its allies have dramatically intensified their support for Ukraine’s air defence capabilities while simultaneously imposing stricter sanctions on Russia, reflecting a deepening commitment to sustaining Kyiv’s resistance amid growing Russian missile and drone assaults.
Enhanced Air Defences for Ukraine
Over the past week, Ukraine’s European partners mobilized significant resources to bolster the country’s defences against an escalating barrage of Russian drones and ballistic missile strikes. This concerted effort is shaped both by urgent operational needs on the ground and the strategic imperative to weaken Moscow’s warfighting capacity.
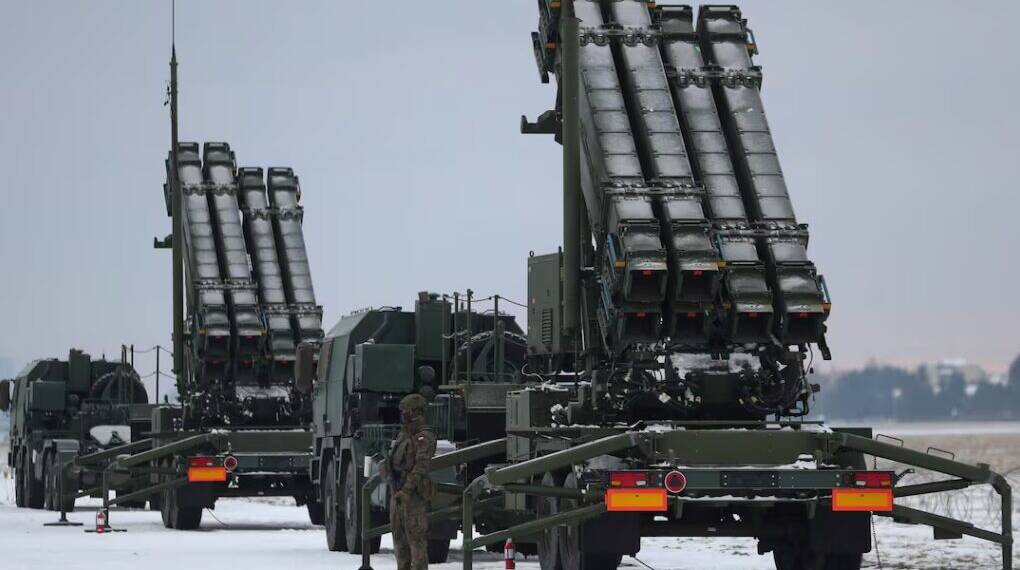
Germany and the United States have agreed to deliver five Patriot surface-to-air missile systems to Ukraine. These systems represent the only effective defence Ukraine currently possesses against Russia’s deadliest long-range ballistic missiles. The Patriot system includes radar arrays and launch vehicles capable of detecting and intercepting a diverse range of airborne threats, particularly high-end ballistic missiles, making it one of the world’s most capable air defence solutions.
Germany’s Defence Minister Boris Pistorius confirmed this agreement following diplomatic coordination with US Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth, with Germany funding the delivery. As a reciprocal arrangement, the US will prioritize Germany and other donors in their acquisition of replacement Patriots.
In addition to the Patriots, the United Kingdom and Germany committed to jointly supplying Ukraine with air defence missiles to reinforce its ability to counter constant drone attacks. Ukraine currently employs a mix of advanced missile defence systems, including the German-made IRIS-T and US-made NASAMS and SHORAD, which have gained particular prominence as drone warfare has intensified. Between July 17 and 22 alone, Ukraine intercepted or electronically suppressed 833 out of 968 unmanned aerial vehicles launched against critical infrastructure, reflecting both the scale of the threat and the growing sophistication of Kyiv’s defences.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy has emphasized increasing domestic arms production as a strategic priority, aiming to raise locally produced weapons’ share from 40% to at least 50% within six months. This domestic effort focuses heavily on drone and interceptor technologies, notably including radar-assisted anti-aircraft guns like the Gepard 35mm and indigenous interceptor drones. Zelenskyy’s vision also highlights collaboration with European partners to develop an integrated air defence infrastructure, underscoring Ukraine’s role not just as a recipient but also a contributor to regional security.
Despite these defensive gains, Ukraine remains vulnerable to Russian missile strikes. The threat is compounded by Russia’s deployment of volley attacks using drones, ballistic missiles such as the Kh-47M2 Kinzhal, cruise missiles, and Iskander-K systems. Recent attacks have involved hundreds of drones launched overnight, with Russia reportedly planning to escalate to thousands in future strikes. Ukraine’s reliance on external systems like the Patriot underlines a critical gap in its ability to counter high-end ballistic threats fully. The rapid deployment of additional Patriots and expanded European defence budgets is thus crucial.
Strategic European Defence Initiatives
The European Union is responding not only with direct military assistance but also by bolstering its own collective defence framework. On July 16, EU Commission President Ursula von der Leyen proposed a fivefold increase in the EU’s common defence budget for 2028-2034, escalating it to €131 billion ($154 billion).
These funds will accelerate investment in European defence industries, research, cybersecurity, and dual-use infrastructure, aiming to reduce reliance on external support and enhance strategic autonomy. A proposed European Competitiveness Fund will further drive innovation in military technology, enhancing readiness for future conflicts.
The EU also pledged to double its Ukraine Assistance Fund to €100 billion ($117 billion), emphasizing sustained financial backing for Kyiv amid a protracted war.
Tightened Sanctions Targeting Russian Energy and Finance
Simultaneous with military support, the EU announced its 18th sanctions package against Russia, targeting the final remnants of Russian energy imports valued at approximately €23 billion ($27 billion). This package includes several novel and stringent measures:
The longstanding price cap on Russian oil was lowered from $60 to $47.60 per barrel, with a dynamic mechanism adjusting it 15% below market prices every six months to constrain Russia’s revenue.
Refined oil products originating from Russian crude are now banned from EU entry, addressing previous refinement loopholes.
The EU expanded its blacklist of vessels comprising Russia’s “shadow fleet” to 444, barring these tankers from EU ports and services to obstruct clandestine oil shipments.
Russian banks blacklisted from doing transactions with the EU increased from 23 to 45, alongside sanctions on dozens of companies aiding Russia’s sanction circumvention, including 11 based outside Russia.
Explicit prohibitions on transacting with the damaged Nord Stream I and II pipelines ensure permanent decommissioning and financial insolvency for those projects.
The United Kingdom, coordinating closely with the EU, adopted matching sanctions and price caps, reinforcing a united front against Russian fossil fuel exports. British officials emphasized the importance of joint actions to “combat those callously fuelling the fires of destruction in Ukraine”.
Operational and Tactical Context
These military and financial measures come amid intensifying combat and aerial confrontations. On July 17, Russian forces made localized gains in multiple Ukrainian regions, seizing towns in Kharkiv, Donetsk, and Zaporizhia. Yet Ukrainian forces have maintained their front lines and conducted effective long-range strikes into Russian territory.
Ukrainian drones struck key military-industrial targets near Moscow, including aviation plants producing MiG fighters and anti-aircraft missile manufacturers. They also damaged critical infrastructure such as a gas pipeline supplying Russian military facilities deep inside Russia.
Simultaneously, Russian air defences reported shooting down dozens of Ukrainian drones near Moscow, illustrating the fierce aerial contest.
Diplomatic and Strategic Implications
While diplomatic efforts continue, including resumed Istanbul peace talks, Western and Ukrainian leaders recognize that military preparedness and economic pressure remain central to sustaining Ukraine’s defense and weakening Moscow’s warfighting capacity. The symbolic re-engagement of the US in the Ukraine Defence Contact Group, albeit without taking on donor status, reflects a nuanced transatlantic dynamic where European nations are increasingly assuming leadership and financial burdens of supporting Kyiv’s defence.
Furthermore, NATO and US commanders warn of a broader potential global conflict involving simultaneous Russian and Chinese offensives in Europe and Taiwan within 18 months, adding urgency to European defence modernization.
The EU’s stepped-up air defence support for Ukraine including Patriot missile deployments and coordinated mass supply of air defence missiles addresses critical capability gaps in intercepting lethal ballistic and drone threats. Complemented by historic sanction packages targeting the last vestiges of Russian energy revenues and deepening European defence budgets, these measures reflect a multi-dimensional strategy to sustain Ukraine’s resistance.
At the tactical level, this bolsters Ukraine’s resilience against Russia’s intensifying missile and drone campaigns. Strategically, it signals Europe’s determination to enhance its defence autonomy and integrate Ukraine more closely into its security architecture, while economically choking Russia’s war financing.
However, persistent Russian territorial advances and Moscow’s capacity to launch extensive aerial offensives mean the conflict remains perilous and protracted, requiring sustained international resolve and evolving support to prevent further escalation and pave a potential path toward peace.