Welcome, students, parents or teachers in this article we are going to give you 10 Difference between western Ghats and eastern Ghats. Take a note that in exams you can add more points in answer to score more. To earn extra marks you can explain it in about 300 words. Thanks for reading the answer.
10 Difference between western Ghats and eastern Ghats
Here is the list of 10 Difference between western Ghats and eastern Ghats with explanation:
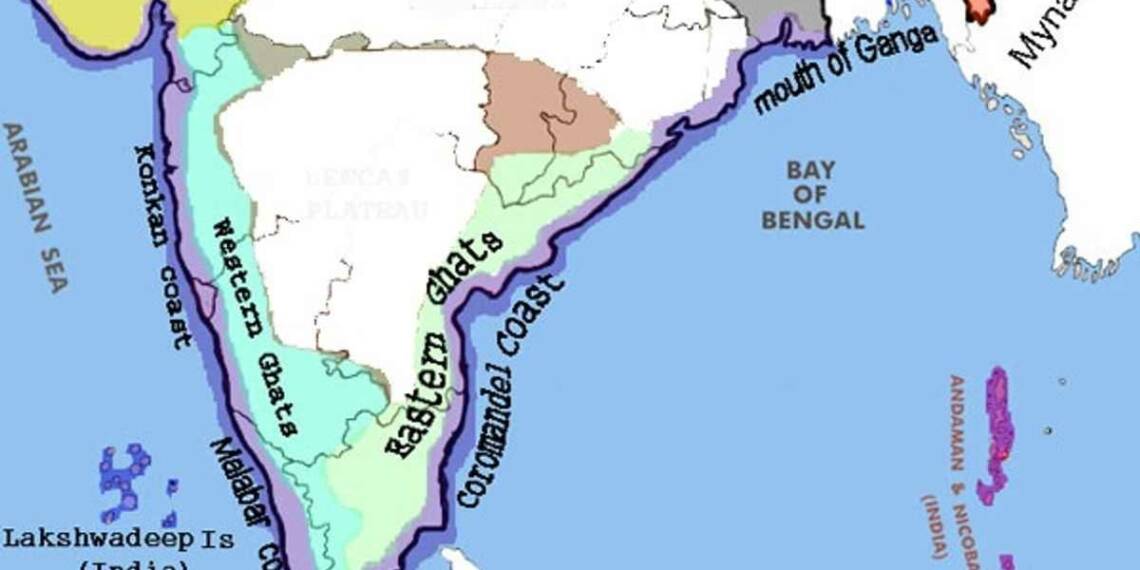
Location: The Western Ghats are located in the western part of India, while the Eastern Ghats are located in the eastern part of India.
Elevation: The Western Ghats are higher in elevation compared to the Eastern Ghats. The highest peak in the Western Ghats is Anai Mudi (2695 m) while the highest peak in the Eastern Ghats is Mahendragiri (1501 m).
Climate: The Western Ghats have a humid and tropical climate, while the Eastern Ghats have a dry and tropical climate.
Vegetation: The Western Ghats are known for their dense forests and rich biodiversity, while the Eastern Ghats are known for their dry deciduous forests and scrublands.
Endemism: The Western Ghats are known for their high levels of endemism, with many species found only in this region, while the Eastern Ghats have lower levels of endemism.
Human impact: The Western Ghats have been heavily impacted by human activity, including deforestation and mining, while the Eastern Ghats have seen less human impact.
Also Read: Bring these 9 indoor plants for positivity in the house
Tourist Attractions: The Western Ghats are a popular tourist destination, known for their scenic beauty and wildlife, while the Eastern Ghats are less popular and less developed as a tourist destination.
Geographical Location: The Western Ghats are located along the western coast of India, while the Eastern Ghats are located along the eastern coast of India.
Elevation: The Western Ghats are generally higher in elevation than the Eastern Ghats. The highest peak in the Western Ghats is Anamudi, which stands at an elevation of 2,695 meters. In contrast, the highest peak in the Eastern Ghats is Mahendragiri, which stands at an elevation of 1,501 meters.
Vegetation: The Western Ghats are known for their rich biodiversity and are home to a wide variety of flora and fauna. They are also known for their tropical evergreen forests and are a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The Eastern Ghats, on the other hand, have a dry deciduous forest cover and are less biodiverse than the Western Ghats.
Also Read: Difference between Rabi and Kharif crops and Definition